Auto-remediate insecure cloud resources with AI
Many organizations have strict policies requiring that all cloud resources meet specific security standards:
- Data storage must be encrypted at rest
- S3 buckets must not be publicly accessible
- ElastiCache must have deletion protection enabled
- RDS instances must be private and encrypted
Relying on manual checks or ad-hoc fixes is error-prone and delays remediation. With Port + Claude Code, you can enforce policies at creation time and generate infrastructure-as-code (IaC) patches automatically.
This guide demonstrates how to create an AI-powered system that automatically detects insecure cloud resources and generates Terraform patches to remediate security violations.
Common use cases
- Enforce security policies by detecting and fixing unencrypted storage, public access, or missing deletion protection
- Reduce manual security reviews by automating the detection and remediation of common misconfigurations
- Maintain compliance by ensuring all cloud resources meet security requirements automatically
Prerequisites
This guide assumes the following:
- You have access to Port and have completed the onboarding process
- You have installed Port's AWS integration (or GCP/Azure)
- You have completed the setup in the Trigger Claude Code from Port guide
While this guide focuses on AWS RDS instances and uses Claude Code, the same approach can be applied to other cloud providers and resource types by adjusting the blueprint schemas and security policies. You can also use other AI coding agents like GitHub Copilot or Gemini to generate the infrastructure-as-code patches.
Set up data model
We need to create blueprints to support our cloud resource security workflow. These blueprints will track cloud resources and their security compliance status.
Create RDS Instance blueprint
When installing the AWS integration in Port, the AWS Account blueprint is created by default.
However, the RDS Instance blueprint is not created automatically so we will need to create it manually.
-
Go to the builder page of your portal.
-
Click on
+ Blueprint. -
Click on the
{...} Edit JSONbutton. -
Copy and paste the following JSON configuration:
RDS Instance blueprint (Click to expand)
{
"identifier": "rdsInstance",
"description": "This blueprint represents an AWS RDS DBInstance in our software catalog",
"title": "RDS Instance",
"icon": "AWS",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"link": {
"type": "string",
"format": "url",
"title": "Link"
},
"dbInstanceClass": {
"type": "string",
"title": "DB Instance Class"
},
"dbInstanceStatus": {
"type": "string",
"title": "DB Instance Status"
},
"engine": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Engine"
},
"storageType": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Storage Type"
},
"engineVersion": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Engine Version"
},
"port": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Port"
},
"allocatedStorage": {
"type": "number",
"title": "Allocated Storage"
},
"endpoint": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Endpoint"
},
"multiAZ": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Multi-AZ"
},
"deletionProtection": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Deletion Protection"
},
"availabilityZone": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Availability Zone"
},
"masterUsername": {
"type": "string",
"title": "Master Username"
},
"publicAccess": {
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Public Access"
},
"vpcSecurityGroups": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string"
},
"title": "VPC Security Groups"
},
"arn": {
"type": "string",
"title": "ARN"
},
"storageEncrypted": {
"icon": "DefaultProperty",
"type": "boolean",
"title": "Storage Encrypted"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"aggregationProperties": {},
"relations": {
"account": {
"title": "Account",
"target": "awsAccount",
"required": true,
"many": false
}
}
} -
Click
Createto save the blueprint.
Update integration mapping
-
Go to the data sources page of your portal.
-
Select the AWS integration.
-
Add the following YAML block into the editor to ingest storage data from AWS:
AWS integration configuration (Click to expand)
deleteDependentEntities: true
createMissingRelatedEntities: true
enableMergeEntity: true
resources:
- kind: AWS::Organizations::Account
selector:
query: 'true'
port:
entity:
mappings:
identifier: .Id
title: .Name
blueprint: '"awsAccount"'
properties:
arn: .Arn
email: .Email
status: .Status
joined_method: .JoinedMethod
joined_timestamp: .JoinedTimestamp | sub(" "; "T")
- kind: AWS::RDS::DBInstance
selector:
query: 'true'
useGetResourceAPI: 'true'
port:
entity:
mappings:
identifier: .Identifier
title: .Properties.DBInstanceIdentifier
blueprint: '"rdsInstance"'
properties:
link: >-
'https://console.aws.amazon.com/go/view?arn=' +
.Properties.DBInstanceArn
dbInstanceClass: .Properties.DBInstanceClass
dbInstanceStatus: .Properties.DBInstanceStatus
engine: .Properties.Engine
storageType: .Properties.StorageType
engineVersion: .Properties.EngineVersion
port: .Properties.Endpoint.Port
allocatedStorage: .Properties.AllocatedStorage
endpoint: .Properties.Endpoint.Address
multiAZ: .Properties.MultiAZ
deletionProtection: .Properties.DeletionProtection
availabilityZone: .Properties.AvailabilityZone
masterUsername: .Properties.MasterUsername
publicAccess: .Properties.PubliclyAccessible
vpcSecurityGroups: .Properties.VpcSecurityGroups
arn: .Properties.DBInstanceArn
instance_id: .Properties.InstanceId
relations:
account: .__AccountId -
Click
Save & Resyncto apply the mapping.
Set up automations
We will create an automation that triggers when a new RDS instance is added to the catalog and violates security policies.
Create insecure RDS detection automation
This automation monitors RDS instance creation and triggers remediation when security violations are detected:
-
Go to the automations page of your portal.
-
Click on
+ Automation. -
Click on the
{...} Edit JSONbutton. -
Copy and paste the following JSON configuration:
Insecure RDS detection automation (Click to expand)
Repository configurationReplace
<YOUR-IAC-REPOSITORY>with your actual infrastructure repository name in the format<github-org>/<repo-name>. This should match the repository identifier used in your Service blueprint mapping.{
"identifier": "insecure_rds_creation",
"title": "Insecure RDS Creation",
"description": "Automation that remediates insecure RDS instances (missing deletion protection, storage encryption, or private access) using IaC.",
"icon": "AmazonRDS",
"trigger": {
"type": "automation",
"event": {
"type": "ENTITY_CREATED",
"blueprintIdentifier": "rdsInstance"
},
"condition": {
"type": "JQ",
"expressions": [
".diff.after.properties.deletionProtection == false",
".diff.after.properties.storageEncrypted == false",
".diff.after.properties.publicAccess == true"
],
"combinator": "or"
}
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "WEBHOOK",
"url": "https://api.getport.io/v1/actions/run_claude_code/runs",
"agent": false,
"synchronized": true,
"method": "POST",
"headers": {
"RUN_ID": "{{ .run.id }}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"body": {
"properties": {
"service": "<YOUR-IAC-REPOSITORY>",
"prompt": "Here is the current configuration of the RDS instance: {{ .event.diff.after }}.\n\nGenerate a Terraform patch that remediates the following misconfigurations:\n1. Ensure the RDS instance is not publicly accessible (set publicly_accessible = false).\n2. Enable deletion protection (set deletion_protection = true).\n3. Ensure storage is encrypted (set storage_encrypted = true).\n\nThe Terraform must:\n- Be compatible with the existing AWS provider configuration.\n- Preserve existing identifiers (db_instance_identifier).\n- Only update the relevant security fields.\n- If an existing RDS file (e.g., rds.tf or main.tf) exists, append the fix there\n- If no such file exists, create a new file named rds_remediation.tf\nDo not overwrite unrelated files.\n\nAfter generating the code, open a PR with a description summarizing what was fixed and why."
}
}
},
"publish": true
} -
Click
Createto save the automation.
This automation triggers on any RDS instance creation that violates security policies. You can modify the condition to be more specific or add additional security checks based on your organization's requirements.
Test the workflow
To test the remediation workflow:
-
Create (or ingest) a cloud resource such as RDS instance that violates one of the policies (e.g.,
publicAccess = true). -
Port will trigger the automation automatically.
-
Claude Code generates a Terraform patch and opens a pull request in your repository.
-
Review and merge the PR.
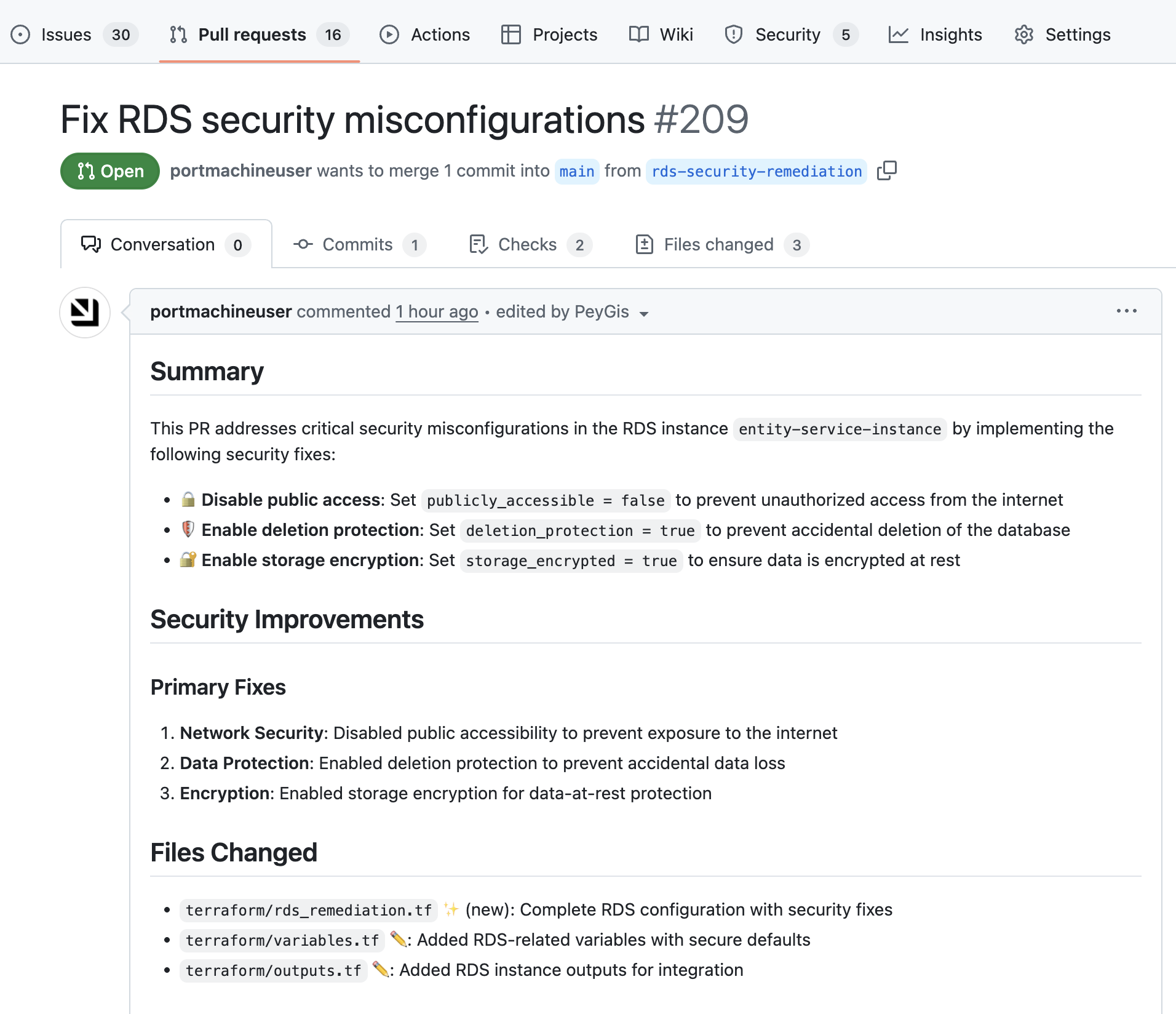
Extend to other resource types
You can extend this approach to other cloud resources by creating similar blueprints and automations:
S3 Bucket security
Create an S3 bucket blueprint with properties like:
publicAccessBlockencryptionAtRestversioningEnabled
ElastiCache security
Create an ElastiCache blueprint with properties like:
deletionProtectionencryptionAtRestnetworkType
Security Group rules
Create a security group blueprint to monitor for overly permissive rules:
ingressRulesegressRulescidrBlocks